Whether it’s a headline-grabbing ransomware attack or a quiet data breach that leaks sensitive customer information, cyberattacks can jeopardize trust in an organization, disrupt its operations, and cause lasting damage.
Information security (InfoSec) is the practice of safeguarding your organization’s most valuable data. Whether it’s customer data, intellectual property, or internal communications, InfoSec ensures your information stays protected from unauthorized access, disclosure, or destruction.
What Is Information Security?
At its core, information security is about protecting information assets using a holistic discipline that combines people, processes, and technology to safeguard data from threats.
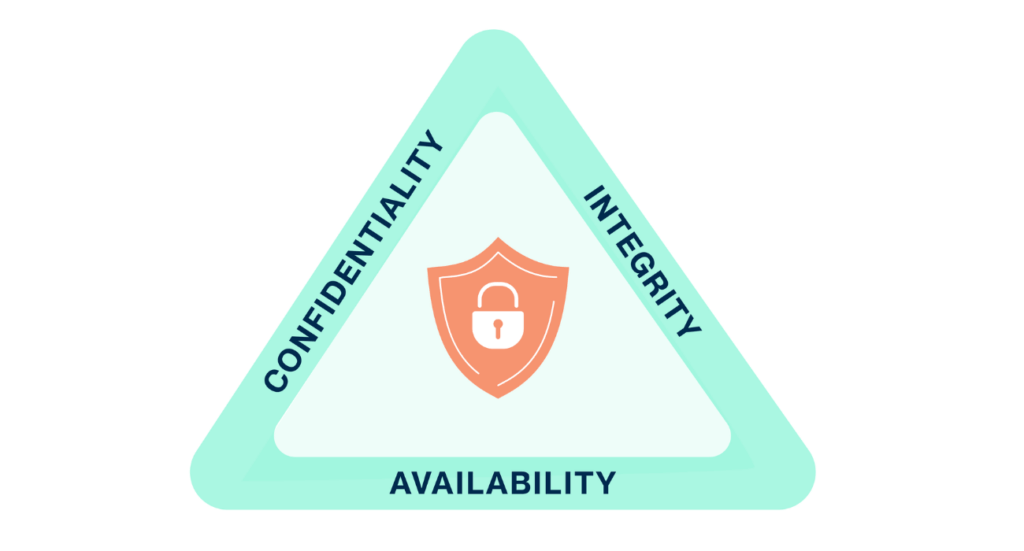
One of the foundational concepts in InfoSec is the CIA Triad:
- Confidentiality: Ensuring sensitive data is accessible only to authorized users. This may include, for example, encrypting customer data.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and trustworthiness of data. This may include controls to prevent a user from making unauthorized changes to financial records.
- Availability: Making sure information and systems are accessible when needed. This can include systems and tools designed to ensure a customer portal stays online.
It’s also important to understand how cybersecurity fits into this picture. While InfoSec covers all forms of information, including paper records and verbal communications, cybersecurity focuses specifically on protecting digital assets such as networks, systems, and data.
Why Does InfoSec Matter?
On an organizational level, safeguarding sensitive information (such as customer data and intellectual property) is critical. A single data breach can erode customer confidence while, in contrast, demonstrating robust InfoSec practices helps your organization earn and retain stakeholder trust.
Effective InfoSec also plays valuable roles in ensuring business continuity. Downtime from a security incident can halt operations, but strong InfoSec policies and procedures can help an organization promote resilience and minimize disruptions.
Similarly, InfoSec helps organizations meet regulatory compliance obligations. Laws like the European Union’s GDPR and HIPAA in the United States impose strict data protection requirements. Compliance isn’t optional—it’s a necessity to avoid fines and regulatory inquiries.
On a broader societal level, strong InfoSec practices also protect critical infrastructure, combat cybercrime and terrorism, and foster a secure environment for innovation and economic growth.
Key Areas Within InfoSec
InfoSec isn’t a single action—it’s a collection of practices across different domains that work together to protect your organization’s data, systems, and reputation. Effective security requires a continuous process that spans policies, technology, people, and procedures.
From identifying risks and implementing controls to monitoring systems and responding to incidents, each step builds on the other to create a resilient defense. This layered approach is designed to ensure that if one safeguard fails, others remain in place to protect your critical assets—reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing your organization’s ability to adapt to evolving threats.
Key aspects of InfoSec include:
- Network Security: Protects your IT networks from unauthorized access or attacks
- Endpoint Security: Secures devices like laptops and smartphones that connect to your network
- Data Security: Protects data at rest, in transit, and in use through encryption and access controls
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Ensures only authorized users access specific resources
- Application Security: Embeds security into the software development lifecycle
- Cloud Security: Applies security best practices to data and services in the cloud
- Incident Response: Prepares your organization to respond effectively to security incidents
- Security Awareness and Training: Educates your team on threats like phishing and social engineering.
The Role of InfoSec Frameworks
Frameworks give structure to your InfoSec efforts, helping you meet industry standards and build trust with customers and partners. By aligning with established frameworks like ISO/IEC 27001, NIST CSF, or SOC 2, organizations gain a clear roadmap for identifying risks, implementing controls, and continuously improving their security posture.
These frameworks can help ensure your security measures are comprehensive, consistent, and aligned with regulatory and contractual obligations.
Some of the leading frameworks include:
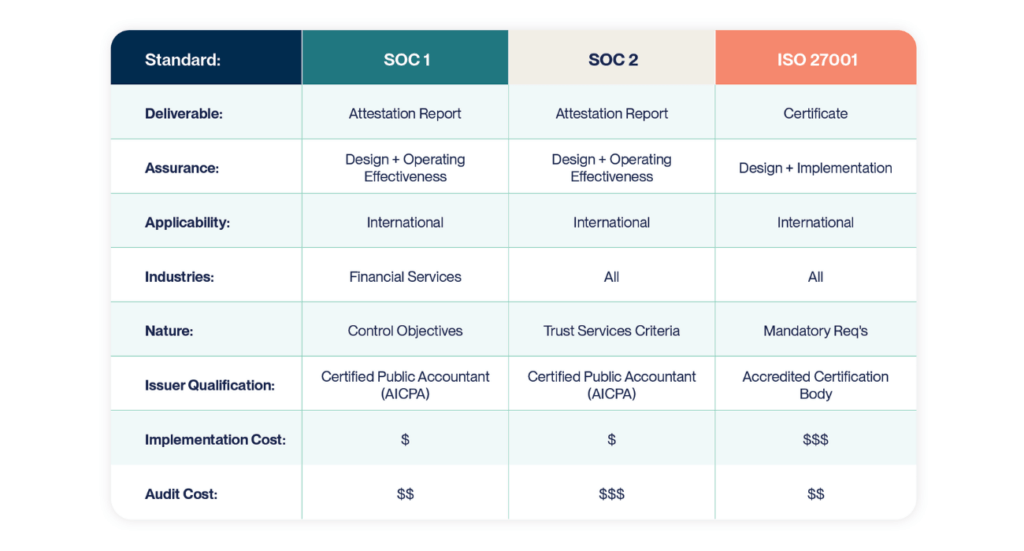
- SOC (System and Organization Controls): These reports allow service providers to demonstrate the effectiveness of their internal controls.
- SOC 1 focuses on financial reporting controls.
- SOC 2—often the most relevant for InfoSec—covers security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- SOC 3 offers a general-use summary for public audiences.
- ISO/IEC 27001: An international standard that guides the creation and maintenance of an Information Security Management System (ISMS), emphasizing a risk-based, process-oriented approach.
- HITRUST: Offers a broad-ranging framework that integrates requirements from more than 40 global data security standards and regulations.
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): Offers a flexible approach to managing cyber risk with five core functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Adopting a recognized framework demonstrates your commitment to safeguarding sensitive information, enhances credibility with stakeholders, and helps you create a competitive advantage in today’s security-conscious marketplace.
By understanding the fundamentals of InfoSec and adopting recognized frameworks, your company can stand out in the marketplace by demonstrating a strong security posture that protects your organization’s reputation as well as your data.
To learn more about the most effective ways to protect your organization and your critical data, contact us.
















