The ISO 27001 certification and the SOC 2 report are perhaps the leading frameworks for companies to demonstrate their commitments to securing customer data. Some service providers, depending on their customers and the types of information they handle, can benefit from obtaining both.
Understanding the uses of each framework, where they overlap, their intended audiences—and whether an organization needs one, the other, or both—can play a large role in helping a service organization enhance its risk management efforts and highlight its security capabilities to current and prospective customers.
What is SOC 2?
A SOC 2 report provides service organizations with an external opinion on their compliance with a standardized set of industry-neutral controls based on the AICPA’s Trust Services Criteria—security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Under SOC 2, only the security criterion is mandatory. Deciding whether to include any of the other criteria depends on the types of information a service provider handles and its customers’ requirements.
SOC 2 is not a certification. Instead, it is an audit opinion on the description of the system (a written narrative describing the infrastructure, data, people, processes, and boundaries of the system), and the controls implemented.
What is ISO 27001?
An ISO 27001 Information Security Management System certification provides service organizations with a framework that’s more prescriptive than the SOC 2 criteria. ISO 27001 helps organizations manage and protect their information assets by developing policies, procedures, and controls to protect information from unauthorized access, alteration, theft, or destruction.
An ISO certification requires a statement of applicability, risk assessment, internal audit, and management review. The certification also prescribes the number of days, primarily based on the organization’s headcount, an audit will require.
Certification vs. Attestation
A key difference between the two is that SOC 2 is not a certification. A SOC 2 report is an attestation by an independent audit firm as to whether the organization under review reasonably meets the standards outlined in the SOC 2 criteria.
Required Information for Each Review
Both reviews look at the following:
- Risk assessment
- Vulnerability management
- Policies and procedures
- Internal controls
- Monitoring and review
- Third-party risk management
- Compliance
ISO 27001 adds the following requirements:
- Statement of applicability
- Internal audit
- Management review
SOC 2 adds the following:
- Written system description
- Higher sample requirements than ISO 27001
- Processing integrity (optional)
The ISO 27001 Process
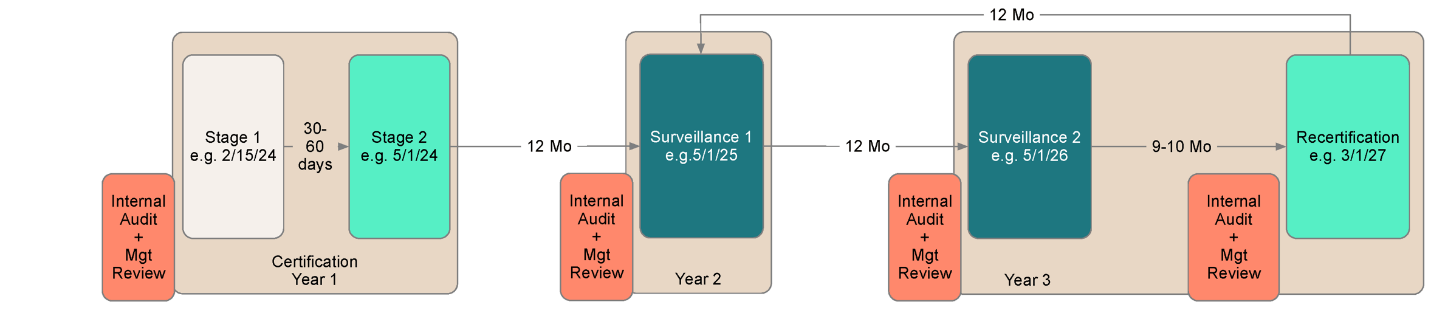
The ISO certification is a three-year certification standard, starting with two stages in the first year. The stage one process is essentially a readiness review to ensure the organization has the information needed for the stage two audit. This will include, for example, items such as the organization’s internal audit function, risk assessment, and key policies and procedures.
If this initial review identifies any areas of concern, the organization will typically have 30 to 60 days to remediate those issues. Once the areas of concern are addressed, the deeper-dive stage two audit will occur.
After an organization receives ISO 27001 certification, surveillance audits are required for two years before its compliance needs to be recertified.
Which Organizations Need ISO Certification?
ISO is an international standard, while SOC 2 focuses on North America. Service organizations supporting international customers outside of North America will benefit from an ISO certification.
Similarly, companies based outside North America hoping to do business in the U.S., Canada, or Mexico will likely have an ISO certification but should consider obtaining a SOC 2 report to capture market opportunities in those markets.
Service organizations operating globally would benefit from undergoing both audits. The good news is the types of information each review requires are similar enough that an organization undergoing one review will be about 70% of the way toward completing the other.
ISO 27001 Internal Audit
Under the ISO 27001 standard, internal audits are required annually and must be conducted by someone who is both competent in auditing against the 27001 standard, as well as independent from the information security management system being reviewed.
Because of these two requirements, most organizations interested in ISO certification outsource their internal audit function to a third party. For all but the largest organizations, someone on staff who is competent in the ISO standard is unlikely to be independent. In addition, outsourcing the internal audit function often results in a more thorough evaluation of their management system.
Optimizing Audit Scheduling
Organizations interested in pursuing ISO 27001 and SOC 2 reviews can streamline the process by scheduling both examinations carefully. For instance, SOC 2’s higher sampling requirement means the information gathered for that audit can also be used as part of the ISO certification, if the audits are timed correctly.
Similarly, the organization should align the periods when auditors will be reviewing evidence with less-busy times of the fiscal year. Conducting both reviews at once can reduce the administrative overhead on their internal teams.
Service organizations that process personal health information and need to demonstrate compliance with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) security and privacy safeguards can also incorporate that examination with a SOC 2 audit.
To learn more about ISO 27001, SOC 2, and the potential benefits of undergoing both reviews, contact us.












